Home Profile
Profile  Product Range
Product Range Industries
Industries Infrastructure
Infrastructure Our Quality
Our Quality Custom Manufacturing
Custom Manufacturing Network
Network Contact Us
Contact Us Send Enquiry
Send Enquiry



Types of Pigment
In today's world, there is a large number of Pigments available. In
fact after the advent of Synthetic Pigments there has evolved various
classes of pigments that are suited to particular types of Industries.
Inorganic Pigments
Inorganic pigments are created through chemical
manufacturing rather than by grinding and washing clays or minerals taken
directly from the earth. The preparation process is also simple and consists
of the steps of washing drying, pulverizing and mixing into a formulation.
They are metallic oxides or synthetics. The following table shows the
refractive index of some of the very popular class of inorganic pigments.
| Pigment |
Refractive Index |
| TiO2 (rutile) |
2.71 |
| TiO2 (Anatase) |
2.55 |
| Antimony Oxide |
2.20 |
| Zinc Oxide |
2.01 |
| Calcium Carbonate |
1.65 |
| Fumed Silica |
1.45 |
Few Examples of inorganic pigments: lead oxide,
cobalt blue, chromium oxide, cadmium yellow, molybdate orange, and nickel
titanate. As new environmental laws are very strict about toxicity a few of
these heavy metal pigments are no longer in use.
Organic Pigments-
Organic Pigments are chemically synthesized, as they are not found in
nature. They contain carbon and comes with relatively low levels of
toxicity, not providing any major environmental concern. Raw materials can
include coal tar and petroleum distillates that are transformed into
insoluble precipitates. They are used as mass colorants and are popular in
plastics, synthetic fibres and as surface coatings-paints and inks. In
recent years the organic pigments are used for hi-tech applications that
includes photo-reprographics, opto-electronic displays and optical data
storage.
Categories of Organic Pigments
Organic pigments are generally categorized into six types :
- Diazo Pigments
- Monoazo Pigments
- Acid and base dye Pigments
- Phthalocyanine Pigments
- Other polycyclic Pigments
- Quinacridone Pigments
Key features and characteristics of Organic Pigments
- Good tinctorial strength
- Cost effectiveness
- Consistency and unique shades
- Completely non-toxic
- Organic pigments shows good color strength
- Very good stability to solvents, light, heat, and weathering
- Very bright, pure, rich colors
Metallic Pigments
Metallic Pigments give bright effects, due to
this they are widely used and are a very popular category of pigments.
Metallic pigments, can be of two types aluminum and zinc.
Aluminium Pigments:
Glittering silver effects are achieved in the widest variety of different
applications by the use of various forms of aluminium pigments. They are
further divided into two categories namely leafing grade and non-leafing
grade. The aluminum pigments are produced from aluminium that has purity in
the range of 99.3-99.97%. The particle has lamellar shape with 0.1-2 um in
thickness and diameter of 0.5-200 um. These pigments founds use in
automotive topcoats.
Some of the preferred applications of Aluminium Pigments are the
following:
- As Reflective paints
- As Corrosion protection coats
- In Marine paints (covering coats)
- Chrome effect paints
- Aerosols
- Roof coatings
- In Heat-proof and highly heat-resistance paints
Zinc Pigments:
The anti-corrosive properties of zinc have been well-known for decades.
Zinc pigments represent an almost ideal combination of the active
anti-corrosive properties of the metal itself with the protective barrier
effect of leaf-shaped pigments.
Zinc Pigments come in two forms of powder and dust. Usually the zinc dust
is finer as compared to powder and is spherical in shape. The dust also has
a light coating of zinc oxide.
The following table cites some popular Zinc Pigments along with their
applications.
| Zinc Pigments |
Application |
| Zinc dust |
Chemical applications Metallurgical applications |
| Zinc phosphate |
Active ingredient in domestic cleaning products |
| Zinc oxide |
Agricultural applications
Rubber industry
Brick kilns
Ceramics |
Industrial Pigments
A few popular pigments have been given below that
have very wide uses:
- CLC Pigments
- DPP Pigments
- Ultramarine Pigments
- Effect Pigments
- Pearlescent
- Fluorescent Pigments
- Inorganic Pigments
- Natural Pigments
- Carbon Black
|
- Organic Pigments
- Organic vs Inorganic Pigments
- Mixed Metal Oxide Pigment
- Phosphorescent
- Pigment Intermediates
- Synthetic Iron Oxide Pigments
- Titanium Dioxide
- Natural Iron Oxide Pigments
|
Refractive index and Classification of pigments
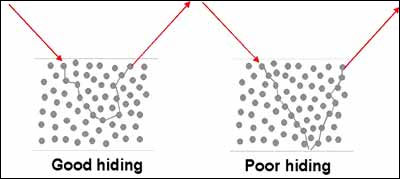
Pigments
are used to give color and protect the substrate. To provide color to a
material pigment should create an opacity. There is a particular limit to
the concentration of pigment particles in a coating determined by the
pigment volume concentration (PVC). This is the reason for having pigment
particles with a high refractive index.
Based on such refractive index, pigments can be divided into two categories
of hiding and extender pigments.
Hiding pigments:
These pigments possess generally refractive index values that are greater
than 1.5. Examples: titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, lithophone etc.
Extender pigments:
These pigments have refractive index values that are close to 1.5.
Examples: calcium carbonate, silica, alkali and alkaline earth metal
silicates etc.
Selection of Pigment and Binder Stability
If you are considering pigmentation of a system,
that is inherently unstable, for example an unstable binder that is to be
pigmented with Titania, the selection of the pigment is then for both
coloration and function. While formulating a colored coating, the pigment's
role should be as an UV absorber or reflector. Thus blocking UV transmission
through the binder, where degradation takes place.
Performance Criteria for commercial organic pigments
The commercial performance of organic pigments
are guided by the following capabilities:
- Coloristic performance
- Durability
- Ecological compatibility
- Tinctorial strength
- Opacity
- Resistance to heat
- Rheological behavior
High
performance organic pigments have high color strength, outstanding fastness
and weatherability properties. They find usage in specialty applications.
Home Profile
Profile
 Product
Range
Product
Range Industries
Industries Infrastructure
Infrastructure Our
Quality
Our
Quality Custom
Manufacturing
Custom
Manufacturing Network
Network Contact
Us
Contact
Us Send
Enquiry
Send
Enquiry

![]() Profile
Profile ![]() Product Range
Product Range![]() Industries
Industries![]() Infrastructure
Infrastructure![]() Our Quality
Our Quality![]() Custom Manufacturing
Custom Manufacturing![]() Network
Network![]() Contact Us
Contact Us![]() Send Enquiry
Send Enquiry


![]()
 Pigments
are used to give color and protect the substrate. To provide color to a
material pigment should create an opacity. There is a particular limit to
the concentration of pigment particles in a coating determined by the
pigment volume concentration (PVC). This is the reason for having pigment
particles with a high refractive index.
Pigments
are used to give color and protect the substrate. To provide color to a
material pigment should create an opacity. There is a particular limit to
the concentration of pigment particles in a coating determined by the
pigment volume concentration (PVC). This is the reason for having pigment
particles with a high refractive index. High
performance organic pigments have high color strength, outstanding fastness
and weatherability properties. They find usage in specialty applications.
High
performance organic pigments have high color strength, outstanding fastness
and weatherability properties. They find usage in specialty applications.![]() Profile
Profile
![]() Product
Range
Product
Range![]() Industries
Industries![]() Infrastructure
Infrastructure![]() Our
Quality
Our
Quality![]() Custom
Manufacturing
Custom
Manufacturing![]() Network
Network![]() Contact
Us
Contact
Us![]() Send
Enquiry
Send
Enquiry